How to edit group policy
How to edit group policy
Group policy is a nice way of managing users and computers. It is an infrastructure in the Microsoft Windows world that is used to centralize and automate the management of configuration or policy settings for users and computers within an Active Directory environment.
You can find more high-level details about group policy at this page: Group policy.
The best way to explain how group policy works is to demonstrate it using an example, but before we show our example, let's find out about the tool that is used to edit or manage group policies.
How to edit group policy?
Before we get to the actual example of setting a policy, we need to explain the tool that is used to access group policies. Group policy can be accessed via the Group Policy Editor. To start the Group Policy Editor, follow the following steps.
Log into the computer using an account that has administrator privileges. This is important. Using just a plain user account will not work well with the Group Policy Editor.
1. Go to the Start menu
2. Click Run
3. Type MMC and hit Enter. (MMC is short for the Microsoft Management Console.)
4. You will see a new window that will be probably blank. At this point you need to add the Group Policy Editor component into the Microsoft Management Console. Go to the File menu.
5. Now select the Add/Remove Snap-in and click Add.
6. Another popup screen will open with the Available Stand-alone Snap-ins menu. Find the Group Policy snap-in in this screen and then click Add. It is possible that you will see Group Policy Object Editor in the menu instead of the Group Policy.
7. The next screen allows you to select which computer policy object you want to access. For now, you want to edit the Local Computer group policy, so just click Finish.
8. Finally click Close and OK to exit the Add/Remove Snap-in dialog box.
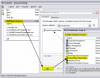
This is what you want to see in the setup screens:
The selected group policy object will be displayed in the Console Root. When you try to exit the Microsoft Management Console, you will be given an option to save your settings. If you save your settings, you will be able to open the Group Policy Editor directly without going through the screens the next time you open MMC.
A quicker way to access the Group Policy Editor
As with many things, there is a quicker way to access the Group Policy Editor. You can open the Group Policy Editor by going to the Start menu, clicking the Run button and executing GPEDIT.MSC. This will get you to the same place like opening the Group Policy snap-in in Microsoft Management Console (MMC).
If you open the Group Policy Editor snap-in from the command line (or the Run menu) via a direct call to the GPEDIT.MSC, it will automatically load the Local Computer Group Policy Object.Group policy example
Knowing how to access the interface for editing and managing group policies, we can take a look at an example. See the Group policy configuration example in Windows XP page.
Windows cannot find 'gpedit'
If you are using Windows XP Home or Windows Vista Home or Windows Vista Home Premium, you will get the "Windows cannot find gpedit" message when trying to run gpedit.msc from the Start -> Run menu. These windows were not designed to join a domain and therefore do not include this tool. If you want to modify any policies in these Windows, you will have to find them in registries. This is true even though Windows Vista references gpedit/secpol in many places in their help.
How to apply local policies to all users except administrators?
Group policies in Windows XP and 2000 applied locally apply to all users on the computer. Group policies cannot be applied via the Group Policy editor GPEDIT to specific users. However, there is a workaround for administrators. You can find more information about this at the following web site:
http://support.microsoft.com/?id=293655
(How to apply local policies to all users except administrators in a workgroup setting in Windows 2000.)
What is the difference between the Group Policy Editor and Local Security Policy Editor?
You can read about the difference on the next page: Difference between gpedit.msc and secpol.msc.
It is easy, just include the code provided below into your HTML code.
 Delicious
Delicious Digg
Digg StumbleUpon
StumbleUpon Furl
Furl Facebook
Facebook Google
Google Yahoo
Yahoo