ISO 27001 (ISO/IEC 27001:2005)
ISO 27001 (ISO/IEC 27001:2005)
ISO 27001 is a standard providing model for an implementation of an effective Information Security Management System (ISMS). ISO 27001 is also known under its more precise name ISO/IEC 27001:2005 and is closely related to another norm known under the name ISO 27002.
Both ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 are together the standards that are used by organizations to implement systems to improve the security of their information and data.
What is ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 or more precisely ISO/IEC 27001:2005 Information technology -- Security techniques -- Specification for an Information Security Management System is an internationally recognized standard that governs the design, implementation, monitoring, maintenance, improvements, and certification in the area of Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). ISO 27001 is not a mandatory law; it is more of a collection of "best practices" and "industry practice proven knowledge" related to ISMS. ISO 27001 is the formal standard against which organizations may seek independent certification of their ISMS. ISO 27001 is a "top down" information management approach.

Picture: The goal of ISO 27001 together with ISO 27002 is to provide a complex information security management system which deals with all areas of your business that have anything to do with information (both directly or indirectly). The picture above shows only a sample of affected areas and business functions. The content of the list depends on your situation.
In general, ISO 27001 says that organizations need to:
- Analyze risks related to information security,
- Define specific and optimal security goals (the standard requires a company to specify its own security goals which an auditor verifies),
- Define methods which all activities should follow (ISO 27001 requires that all activities follow a method; the method is arbitrary, but it is important that the method is well defined and documented),
- Document all risks, goals, and methods (basically everything important needs to be documented),
- Implement measures to mitigate and manage risks (the standard offers a set of security controls, and it is up to the organization to choose which controls to implement based on specific needs of the business),
- Assign accountability for risk management (someone must be responsible),
- Measure information security (a process must ensure continuous verification of all elements of the security system through audits and reviews),
- Embed continuous improvement approach (a process must ensure continuous improvement of all elements of the security system).
Once a management system including the points from the list above is in place, it can be certified. It is clear that such a security management system greatly improves the security of your business.
ISO 27001: Why do I need it?
What happens in your company if vital information gets stolen, your business or trade secret is revealed, or your information system just does not work? Almost everything in today’s business is based on information. Having correct information in the right time is often the source of competitive advantage. Companies spend large portions of their budgets on information acquisition and management. We can say that information is the most precious "asset" a company can have today.
In case you wish to manage and mitigate risks related to working with information and data, you have many options. One of the options is to implement a system for the management of the security of information, so-called Information Security Management System (ISMS). Once processes are in place, you can have your Information Security Management System and your processes certified. Having an ISO 27001 certified Information Security Management System gives you a great advantage in dealing with your customers and partners because it makes you more credible and trustworthy. This can open the door for mutual data and information exchange with your clients, partners, vendors, and customers.Does ISO 27001 involve anyone else besides the IT department?
The IT department is the main executor of an ISO 27001 implementation, but the standard involves almost everyone else too. ISO 27001 implementation is a big project that usually requires big budget. The management of the company needs to be the main driver, sponsor, and promoter of the change. The IT department is usually the ideological and executive force, especially in the IT-related aspects. The management is also the bearer of project implementation risk.
Implementation of specific security measures and policies involves among others the following departments:
- Management (e.g. communication, change management, oversight, motivation),
- HR department (e.g. employee selection process, a formal disciplinary process to handle security breaches, hiring, leaves, and termination),
- Training and education (e.g. development of IT compliance training, HIPAA),
- Building security (e.g. access to premises, access to hardware),
- Building maintenance (e.g. physical hardware security, warehouse, storage, water, power, fire),
- Legal department (e.g. employee agreements and acknowledgements, law suits),
- Vendors and outsourcing (e.g. software standardization, waste paper management),
- And especially employees (e.g. compliance).
The IT department is also involved through penetration testing. External consultants and experts may need to be involved as well.
Does ISO 27001 apply to Information Security or to IT Security?
The scope of the ISO 27001 standard includes many aspects of IT but does not stop there. That is the reason why the main driver of ISO 27001 implementation is not the IT department but the top management of an organization.
ISO 27001 is much broader than just IT; it includes a wider scope. For example, information can be stored on your hard disk and shared through your local network, but it can also be on a paper and shared via your internal mail. ISO 27001 applies to your faxes, copiers, shredders, paper storage, and internal mail as well. These assets or processes are often handled by other than your IT department. This is just a simple example of how ISO 27001 can apply to your business and how it gets beyond the realm of your IT department and "IT security".
How do I market my ISO 27001 certification?
The ISO organization provides strict guidelines for how to market your achievement once you are certified. In short, the pictures below show the most commonly used and allowed ways to inform about your certification.
 or
or ![]()
Picture: The picture above shows the proper way to inform your customers about your certification achievement.

Picture: When marketing your certification, it is prohibited to use the ISO logo.
More details can be found in the Publicizing your ISO 9001: 2000 or ISO 14001: 2004 certification guide downloadable from www.ISO.org. Although this guide is dedicated to former ISO standards, publicizing rules apply the same way to ISO 27001.
What are the benefits of ISO 27001 certification?
A robust audit and certification scheme supports the ISO 27001 standard. ISO 27001 certification is expensive and can take a lot of effort and time, but it also provides many valuable benefits which at the end positively affect your bottom line. The following is a list of some of the benefits. ISO 27001 certification can help you to:
- Map your corporate information system structure (infrastructure, buildings, cabling, environment, alarms, fire and flood prevention, access control, and others),
- Make existing processes more effective or create missing processes (e.g. process for revoking access to employees leaving your company),
- Acknowledge security risks (e.g. only one person has access to critical systems),
- Start active and effective protection against risks (e.g. power surge or power outage protection),
- Protect vital business assets (e.g. backup of accounting database),
- Design ongoing system optimization (e.g. ongoing security audit),
- Maintain lower information technology costs (e.g. managed software patches implementation),
- Create competitive advantage (e.g. improved credibility for your partners and clients),
- Improve your business (e.g. potential data exchange with your clients, ability to apply for government contracts, some major corporations prefer suppliers that can prove they meet best-practice standards, investors and share holders often call for information security),
- Reduce insurance premiums (e.g. insurance premiums can be reduced if you can prove compliance),
- Reduce the potential for law suits (e.g. avoiding customer information being stolen or misused).
As you can see, ISO 27001 certification provides many advantages. In any case, ISO 27001 certification provides an independent assessment of your organization’s conformity to an international standard.
Note, for those already certified against BS 7799, accredited certification bodies establish transitional arrangements.
What is the difference between ISO 27001 and ISO 27002?
ISO 27002 is more of a catalog or a list of recommendations and security considerations that deal with particular information security aspects. However, not to confuse, it is a code of practice containing general good practice guidance rather than prescriptive requirements. The extent to which these security recommendations are implemented in your company and employed by your Information Security Management System depends on the size and needs of your business. You as the orchestrator of your ISO 27001 compliant ISMS are free to choose whichever specific information security controls are applicable to your particular situation.
ISO 27002 encompasses 133 topics divided into 12 chapters which all together provide over 5000 direct or derived security measures intended to improve your Information Security Management System. Responsibility and accountability for these measures can be assigned to selected individuals. These security considerations can be also used as a starting point for your security audit. The information security controls from ISO 27002 are noted in an appendix to ISO 27001.
ISO 27001 is a standard that deals with information security in a broader and bigger-picture sense. ISO 27001 talks about how to implement, monitor, maintain, and continually improve your Information Security Management System (ISMS). ISO 27001 also provides framework for ISO 27001 certification which is practically an audit of your ISMS by a third independent party. ISO 27001 is the "strategy"; ISO 27002 is the "action steps".
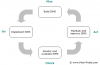
What is the PDCA cycle in ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 implements ISMS through so-called PDCA cycle (Plan – Do – Check – Act). One might think that ISO 27001 implementation is a one-time activity. The opposite is the truth. Once ISO 27001 is implemented, it becomes an ongoing process aiming at continually improving the existing Information Security Management System. It can be depicted in the following picture:
Implementation of ISO 27001 starts with the planning phase. You create a plan, then you implement the solution, but then you also have to monitor results to recommend improvements. This also means that when thinking about ISO 27001 implementation, budgeting should be considered as well: you need both investment budget and an ongoing budget.
Can ISO 27001 be implemented partially?
Since ISO 27001 is a security standard, it has smaller but deeper domain compared to other information security approaches (for example COBIT and ITIL). While for example ITIL handles security by service (that is your IT department can implement IT Service Delivery layer, or IT Release Management layer, or IT Problem Management layer separately as budget permits), ISO 27001 is more of a security framework that implements security through compliance to a security standard. ISO 27001 sees processes in bigger view before they can be implemented partially. So, to make the story short, ISO 27001 is most effective when implemented as a global standard (respective to your organization).
Does ISO 27001 apply to organizations in the USA?
ISO 27001 is a standard that was introduced in the United Kingdom and is widely used in the European Union (EU), India, and Japan.
Companies in the United States do not usually (unless they are global and need to conform to the EU regulation or deal with EU-located clients and customers) implement ISO 27001. A certified ISMS does not guarantee compliance with legislative and local policies but provides a systematic platform to build on. A company that complies with ISO 27001 should be well prepared for compliance with the following U.S. legislative:
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (Section 404),
- SAS/70 requirements,
- HIPAA requirements,
- Gramm Leach Bliley Act of 2002,
- California’s privacy laws including SB 1436.
Once you have the ISO 27001 certification, you are ready to play on the global stage. ISO 27001 is very "popular" for example in India and Japan.
How popular or important is ISO 27001 certification?
ISO 27001 certification is optional, but it is increasingly being demanded from suppliers and business partners by organizations that are concerned about information security. As of August 2008, some 4,700 organizations worldwide have been certified compliant with ISO 27001. The number of ISO 27001 certified organizations grows at a rate of 15-20% annually. You can get an updated list of ISO 27001 certified organizations at www.iso27001certificates.com.
Where can I download ISO 27001?
So, you decided to find out more and download the text of ISO 27001 standard? In general, ISO standards are copyright protected and the ISO organization extends great effort to protect anything it owns. ISO standards are not free. Trying to find a free copy on the web is quite a task, and for understandable reasons, we can't provide a link here. A link to a free copy of the ISO standard can be found occasionally in ISO 27001 related discussion forums.
If you wish to obtain a reliable and up-to-date copy of the ISO 27001 standard it is best to purchase it, either as a standalone copy or as part of a toolkit. Downloadable PDF copies can be found on the web for as little as some $30. When getting the text, make certain you are getting the latest official print and not a draft.
What is the cost and time it takes to get ISO 27001 certified?
The classic consultant answer "it depends" applies. ISO 27001 encompasses everything from locks on your entrance door to what happens with trash under each employee's desk. The cost of ISO 27001 certification will be different in case of a small manufacturing company as compared to an insurance giant. How much auditing will it take? How much penetration testing will you need? How many processes will you need to change? Will you need to run any software/hardware implementations? In general, ISO 27001 certification can cost anywhere from a few tens of thousands dollars to a few hundreds of thousands. Time-wise it can take from a few months to years.
How do I implement ISO 27001?
If you are wondering where you start with ISO 27001 implementation, the ISO 27001 standard defines a 6 stage process which is closely related to the iterative PDCA approach mentioned earlier. The Plan-Do-Check-Act is in quotes a type of a mindset that the company has to acquire to effectively live; it says how to live. The 6 stage process describes what it is the company needs to do to live the ISO 27001 standard.
1) Define an information security policy
First, you have to set the objective of your effort. An information security policy statement expresses management’s commitment to the implementation, maintenance, and improvement of its information security management system. This includes for example email policy, email retention policy, database backup policy, a policy that defines acceptable use of IT equipment, a policy regarding the use of dial-in connections to corporate networks, a policy that defines standards for creating, protecting and changing strong passwords, and so on. (Here is a good ISO 27001 policies website: http://www.dmoz.org/Computers/Security/Policy/Sample_Policies/)
2) Define scope of the information security management system
In this step, you define who are the players and the tools in the game that deal with your security policy.
3) Perform a security risk assessment
Once you know what you want and what the tools and players are, you need to do some testing and find all the holes in your system. Look at the risks that might cause problems to your processes.
4) Manage the identified risk
After finding all security breaches and vulnerabilities, you have to decide how to handle the risk. This includes defining the process owners and the values of your processes. Develop a risk treatment plan.
5) Select controls to be implemented and applied
Knowing how to handle risk factors, you have to find out what to do to eliminate your security holes and vulnerabilities. Think of trainings. One very important factor of successful ISO 27001 implementation is awareness of the involved people.
6) Prepare a Statement of Applicability (SoA)
Now that you went through the whole ISO 27001 process, you need to document it and present findings to your stake holders. The SoA describes the processes, their values, and how you avoid possible risks.
What is the history of ISO 27001?
When British companies analyzed risks related to exchanging information and data with their customers and partners, they discovered that a lot of fraud and security breaches occurred due to the lack of control and auditing. This allowed for many security holes to go unnoticed until a fraud happened.
Based on initiatives of British companies at the end the last century, the United Kingdom Government's Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) wrote the BS 7799 norm which was then published by the British Standards Institute (BSI) in 1995. The BS 7799 norm deals with the security of information systems.
As time went by, it appeared that the BS 7799 and later the revised BS 7799-2 did not address everything that was needed, and so ISO 27001 was introduced in the year 2005. ISO 27001 is the successor to the previous BS 7799. ISO 27001 takes information security to the next level because in addition to approaches for securing information systems, ISO 27001 also addresses IT/IS auditing, management, and processes for continuous improvements.
Where can I get more information?
The ISO 27001 standard is available for purchase for some $110 at the ISO website www.iso.org (go to the Products section and search for 27001) or also for some $30 (downloadable PDF) at the ANSI website webstore.ansi.org.
The following guide explains common IT security audit findings: Top 10 Risk and Security Audit Findings
It is easy, just include the code provided below into your HTML code.
 Delicious
Delicious Digg
Digg StumbleUpon
StumbleUpon Furl
Furl Facebook
Facebook Google
Google Yahoo
Yahoo